Condition
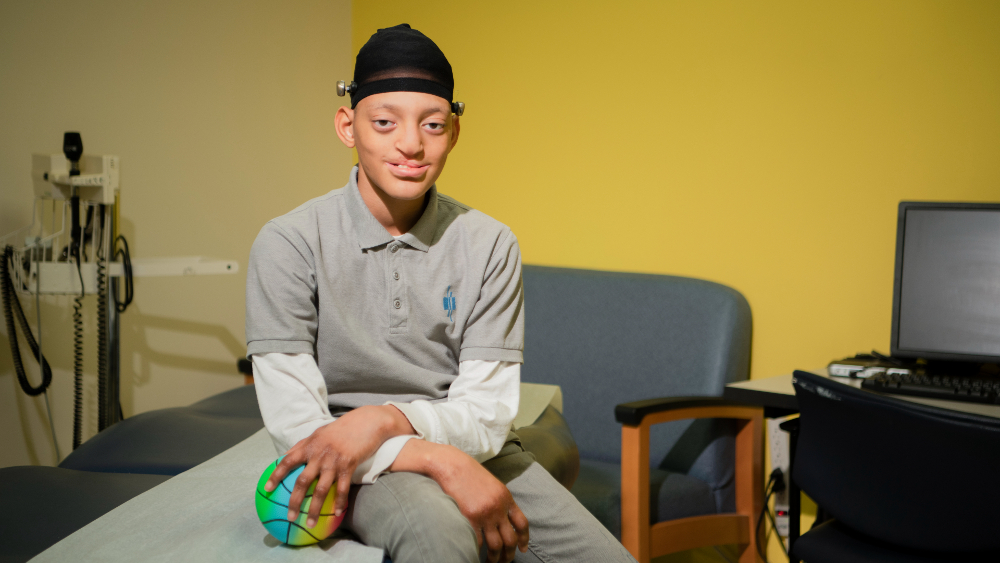
Pediatric Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome
What Is Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome?
Saethre-Chotzen syndrome is a rare genetic (present at birth) condition in which certain sutures (joints) between skull bones grow together too early. This birth defect causes abnormal development in the head and face, which affect their shape.
In most cases of Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, the sutures that are closed are the coronal (from ear to ear) and sometimes the lambdoid (across the back of the head). This condition is called craniosynostosis.
What Causes Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome?
Gene mutations cause Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, and children inherit this genetic disorder from their parents.
Symptoms of Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome
Children with Saethre-Chotzen syndrome may have one or more of these symptoms:
- Misshapen head: short from front to back, long from top to bottom
- High, flat forehead and low hairline
- Bulging, wide-set, and possibly crossed eyes
- Drooping eyelids (ptosis)
- Uneven facial features because of malformed cheekbones and eye sockets
- Small, misshapen ears
- Jaw deformities such as a receding upper jaw or a protruding lower jaw
- Cleft palate (opening in the roof of the mouth)
- Partially fused or webbed, or unusually short fingers or toes
How Is Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome Diagnosed?
Your baby’s pediatrician may notice the distinctive skull and face shapes of Saethre-Chotzen syndrome at birth. After examining and measuring your baby’s head, the pediatrician will use other tests to rule out other, similar syndromes that also have skull deformities.
At Children’s National, the diagnostic tools we may use include:
- X-rays to check for fused (missing) sutures on the sides, back, or other parts of the head, or ridges along these sutures
- Diagnostic imaging, especially CT scans, to check for fluid and pressure inside the skull, fused sutures, or ridges along sutures
- Genetic tests to check for mutations that would indicate this or other syndromes your child may have
Treatments for Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome
Treatment for Saethre-Chotzen syndrome focuses on relieving pressure inside the head and correcting the skull and facial deformities. At Children’s National, our treatment options include:
- Surgery on the skull usually before 18 months of age
- Minimally invasive surgery for infants younger than 3 months to open skull sutures for normal skull and brain growth
- Traditional surgery for infants 6 months or older to correct the skull’s shape
- Surgery to correct deformities of the face, jaw, ears, fingers, or toes
- Orthodontic surgery to correct dental problems
- Speech therapy to help with speech and language development
 Aasha's Rare Gift Will Help Other Babies Grow up Healthy
Aasha's Rare Gift Will Help Other Babies Grow up HealthyTesting the descrption field
Departments that Treat Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome

Rare Disease Institute
Children’s National Rare Disease Institute (CNRDI) is a first-of-its-kind center focused exclusively on advancing the care and treatment of children and adults with rare genetic diseases.




